Multiple RDP sessions is disabled on Windows servers. It means that if you are working on the server and at the same time another administrator connects, you get disconnected, because the other admin takes over. How to enable multiple RDP sessions? There is a simple way to do it and I’ll show you how to do it on single server or on a group of servers (via GPO).
There is many use cases when you need to enable concurrent remote sessions for a Windows system. When working for an organization and using W2008 (R2), W2012 (R2) servers as file systems, DCs, and where you work with several admins in a team, this setting is handy.
For the client systems (XP, Vista, Windows Seven), that’s another story. You would probably won’t do it at your organization, but at home, you do what you want, right? -:). For Windows client based systems you cannot (legally) activate multiple sessions, because it’s restricted by Microsoft. But there are some tools I’ll show ya.
How to enable multiple RDP Sessions – single server option
There is a simple way to do it, but depending if your domain reinforces a single sessions through group policy, you might need to configure that through GPO at the domain level.
To activate concurrent remote sessions on W2012 or W2012R2 (note that this works as well for 2008 and 2008R2)
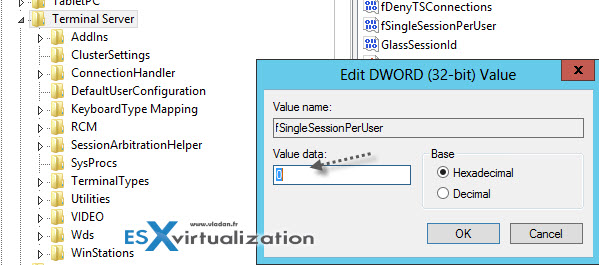
- Go and open regedit and locate the tSingleSessionPerUser key and change the default value from 1 to 0. No need to restart.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal Server
How to enable multiple RDP Sessions on W7 (or Vista, XP) systems.
Here it comes, not legal, but handy… There are several tools which can do the job and allow multiple RDP sessions to a computer (or VM) running W7 or Vista. There is two tools that I stumbled on searching google and I found the reference on Microsoft Technet forums actually. But as it’s marked there, it’s against the Microsoft’s TOS, so as it’s being said there, it’s on your own risk…
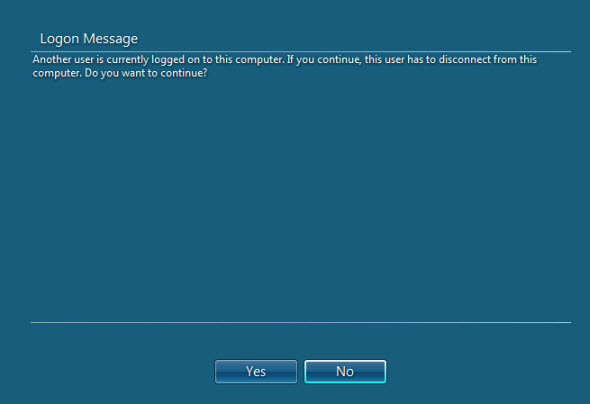
Normally, when you try to connect to Windows 7 system, and someone has already opened a session (locally or remotely), you basically get a screen like this, where you’re asked if you want to disconnect the other user…
I tried both links, but only one worked for my use case. As I’ve been testing on W7 Enterprise – N based VM, the first tool called Concurrent RDP patcher wasn’t supported on that particular Windows type.
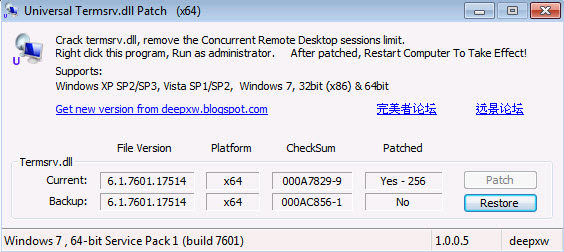
The tool which I retained is a tool called Universal Termsrv.dll patch . It’s working for XP, Vista and W7 based systems, where for the first two there are registry keys and for W7 (x86 and x64) there is a small application, which replaces some dlls (yes, there is a restore option).
Must execute this tool as an admin (right click > execute as an Administrator). You’re prompted for a restart. After reboot, if you re-execute this tool, you got an option to restore your original files, if necessary.
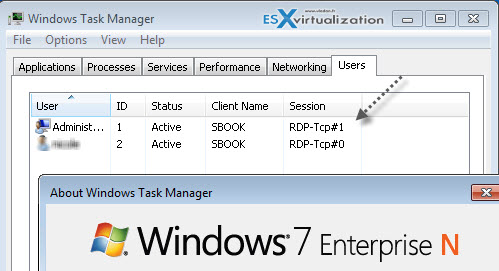
And here is a screenshot showing 2 connections (which one at the console) to a Windows 7 Enterprise – N based VM (x64).
How to enforce a multiple RDP sessions to multiple Windows Servers – through a GPO.
If you’re running Windows Active Directory at your organization and you want to enforce the policy for multiple RDP sessions on a group of servers, you can do it through GPO (Group policy objects). There is many ways you could possibly implement that and it depends on your’s AD structure and your needs. One of the ways (to test it how it works at least) is this one:
- First, in your console for AD users and computers, create a container where you put the computer account, on which one you want the GPO to to apply.
- Move the server computer account through the AD console, to that OU you’v just created.
- Create a new GPO and link it to that container you just created
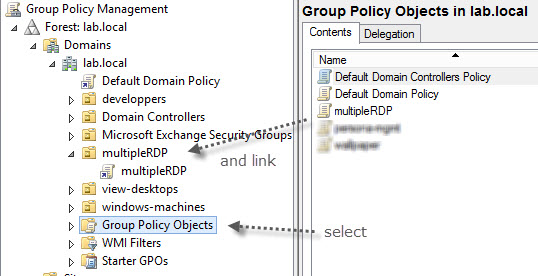
- Modify that GPO (right click the GPO and click modify)
- Go to Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections
- Set the policy called “Restrict Remote Desktop Services users to a single Remote Desktop session” to disable. Close the console.
![]()
- Open command prompt and enter gpupdate /force to force the application of that GPO to your domain.
- Test

